Coffee Roasting and Air Quality Management, Emissions, and Abatement
Air quality management, emissions and abatement, and coffee roasters are all interconnected in ways that are crucial for both the environment and the coffee industry. The coffee roasting process also produces a significant amount of emissions, including carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and other pollutants. These emissions can have negative impacts on the environment and on public health, which is why it is important for coffee roasters to carefully manage their emissions and implement strategies to reduce them.
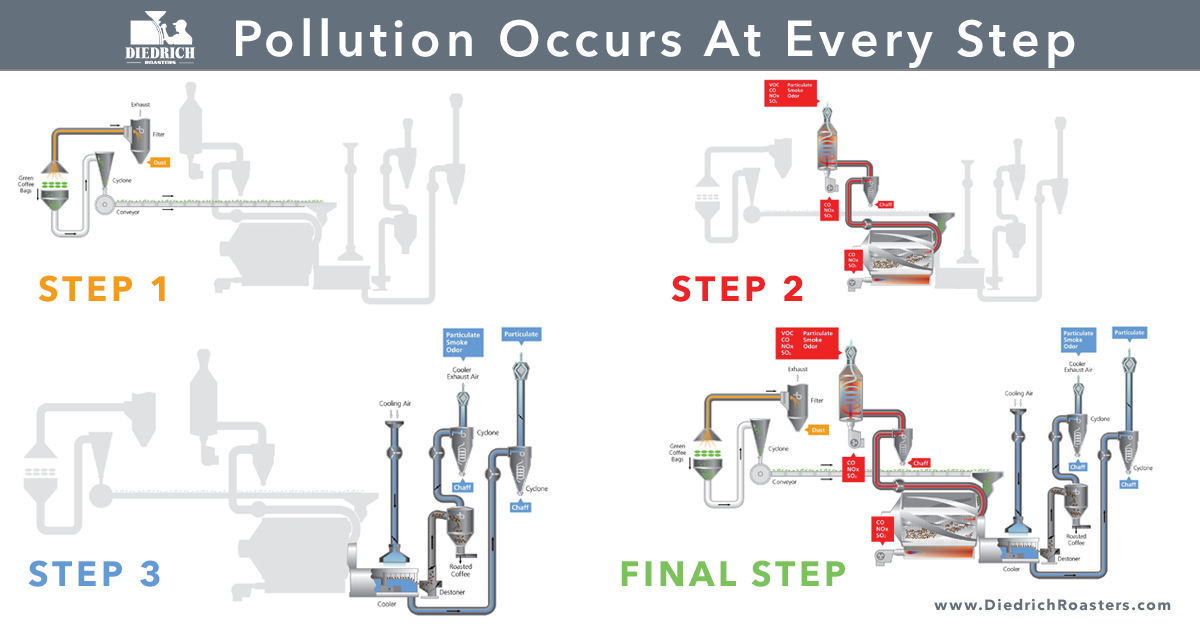
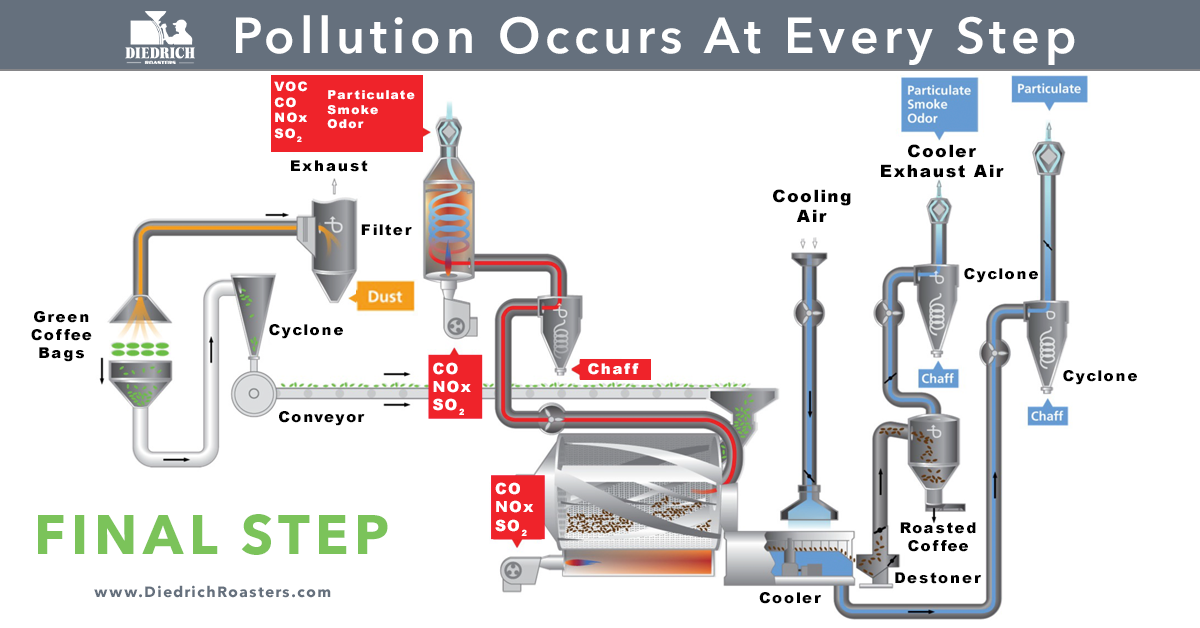
Quality Management: Pollution Occurs at Every Step
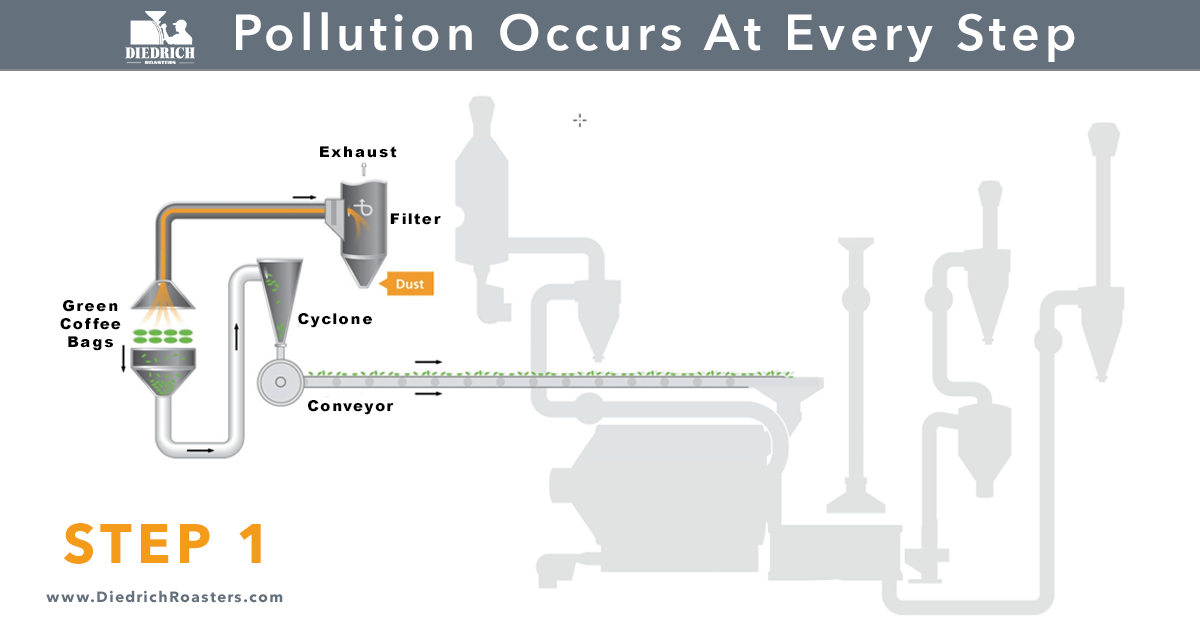
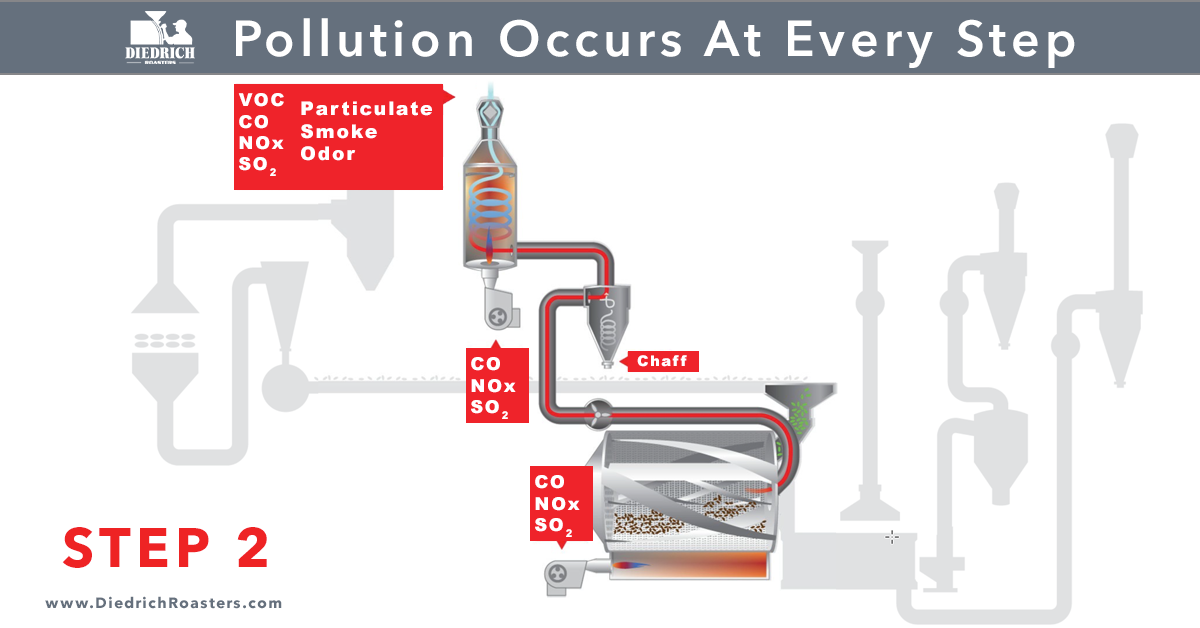
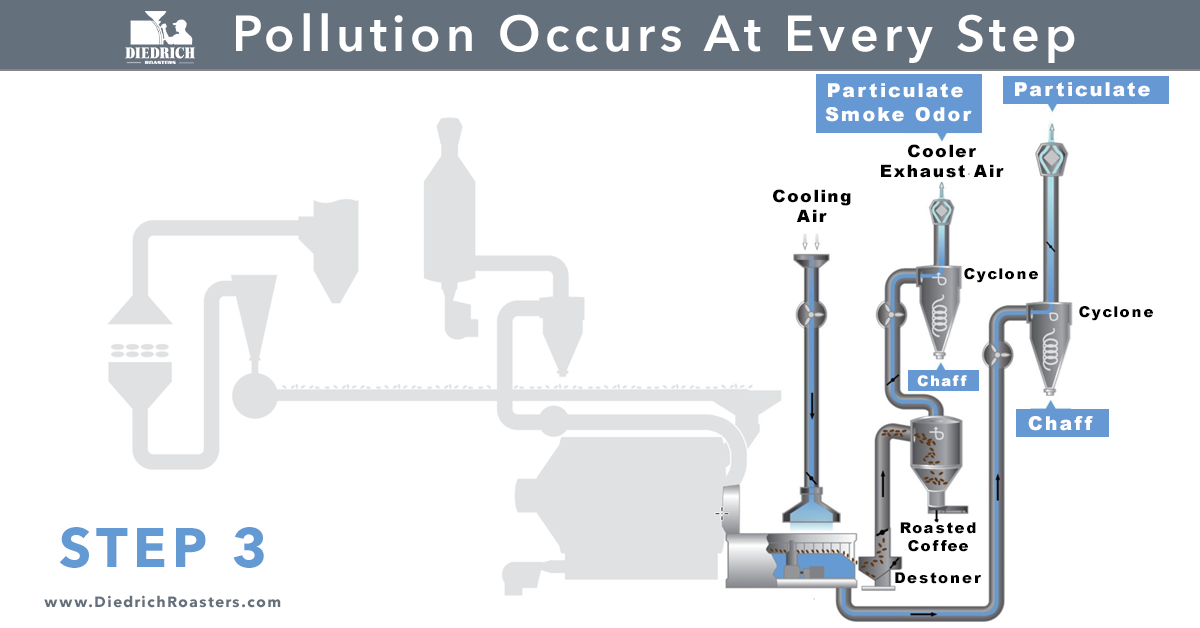
As coffee roasters, it is critical to be aware of the pollution that occurs at every step of the roasting process. Particulate matter, odor, smoke, nitrogen oxides (NOx), carbon monoxide (CO), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) can be emitted and can contribute to various environmental and health issues. In order to be responsible environmental stewards and to avoid fines for violating regulations, it is important to be familiar with the regulations and guidelines set by the various agencies that impose and monitor air toxic emission levels.
Environmental Regulation Agencies
The regulating agencies relevant to you can vary depending on your location. Certain municipalities fall under local air quality management districts that function similarly to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States ot the European Union (EU).
In the United States, there are a number of agencies that impose air toxic emission levels around the country. Most (such as BAAQMD), impose an exposure limit based on the health effect of the given toxic (expressed in units such as ppm and mg/m3). In order to determine whether a new coffee roasting system does not exceed these exposure limits, dispersion modeling is required based on the actual toxins emitted (in the surrounding area—including neighboring companies), the prevailing winds, and the proximity of people.
Some local agencies, such as Washington Administrative Code (WAC) codifies the regulations and arranges them by subject or agency. The online version of the WAC is updated twice a month. These include Title 388 · Title 182 · Title 296 · Title 246. The Puget Sound Clean Air Agency (PSCAA) is another agency that periodically updates its regulations. Articles and Sections on the PSCAA website marked with an asterisk (*) were revised recently and are effective as of November 1, 2022. If you previously downloaded a set of regulations, you only need to download the recent updates.
These agencies and others manage the exposure limits by imposing “trigger” emission levels so a coffee roaster can determine whether their toxic emissions are trivial or sufficiently minor to avoid any dispersion modeling. Most coffee roasters currently fall within the minor toxic levels, but larger facilities can exceed the trigger levels to warrant dispersion modeling.
Depending on your location, you may also need to adhere to specific requirements set by your Iocal air quality management districts. It’s important for roasters to be aware of and comply with the regulations in your area.
The Federal agencies that provide exposure limits include:
- EPA’s Integrated Risk Information System (IRIS)
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR)
- American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists (ACGIH)
- CDC’s National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH)
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA)
Some of the state agencies that provide exposure limits include:
For additional information for determining your environmental compliance needs for your area, please reach out to the Diedrich team.
M-F 8:30am -5:00 pm Central Time
